 ℹ️ Available today with LaunchFast Starter Kits
ℹ️ Available today with LaunchFast Starter Kits
In this guide, you will learn how to deploy an Astro SSR project to AWS Amplify. You will go through the process of setting up a new Astro project, enabling server-side rendering using AWS Amplify adapter, and finally deploying it to AWS Amplify.
Table Of Contents
- Prerequisites
- Create a new Astro application
- Getting Started with the AWS Amplify Adapter for Astro
- Deploy to AWS Amplify
- Conclusion
Prerequisites
You’ll need the following:
Create a new Astro application
Let’s get started by creating a new Astro project. Open your terminal and run the following command:
npm create astro@latest my-appnpm create astro is the recommended way to scaffold an Astro project quickly.
When prompted, choose:
Emptywhen prompted on how to start the new project.Yeswhen prompted if plan to write Typescript.Strictwhen prompted how strict Typescript should be.Yeswhen prompted to install dependencies.Yeswhen prompted to initialize a git repository.
Once that’s done, you can move into the project directory and start the app:
cd my-appnpm run devThe app should be running on localhost:4321.
Next, in your first terminal window, run the command below to install the necessary libraries and packages for building the application:
npm install dotenvThe libraries installed include:
dotenv: A library for handling environment variables.
Getting Started with the AWS Amplify Adapter for Astro
Before deploying your Astro project, you need to install the astro-aws-amplify adapter. This is easily done via the Astro CLI:
npm install astro-aws-amplifyThe libraries installed include:
astro-aws-amplify: An adapter that prepares Astro websites to be deployed on AWS Amplify.
Once the adapter is installed, you’ll need to add it to your astro.config.mjs file. Open the file and add the following code:
import { defineConfig } from 'astro/config';import awsAmplify from 'astro-aws-amplify';
export default defineConfig({ output: "server", adapter: awsAmplify(),});The additions do the following:
- Imports default export of
astro-aws-amplify. - Uses the above import as the
adapterof your Astro application. - Sets
outputtoserverto enable server-side rendering compatible output.
Then, create a amplify.yml at the root of repository with the following code:
version: 1frontend: phases: preBuild: commands: - npm ci build: commands: - env >> .env - npm run build - mv node_modules ./.amplify-hosting/compute/default - mv .env ./.amplify-hosting/compute/default/.env artifacts: baseDirectory: .amplify-hosting files: - '**/*' cache: paths: - node_modules/**/*The code above does the following:
- Uses
preBuildcommands to install the dependencies of your Astro project. - Uses
buildcommands to:- Store all the environment variables into
.envfile at the root of the project. - Build your Astro application.
- Move the
node_modulesdirectory and.envfile to Amplify’s compute directory.
- Store all the environment variables into
Deploy to AWS Amplify
The code is now ready to deploy to AWS Amplify. Use the following steps to deploy:
-
Start by creating a GitHub repository containing your app’s code.
-
Then, navigate to the AWS Amplify Dashboard and click on Get Started under Host your web app section.
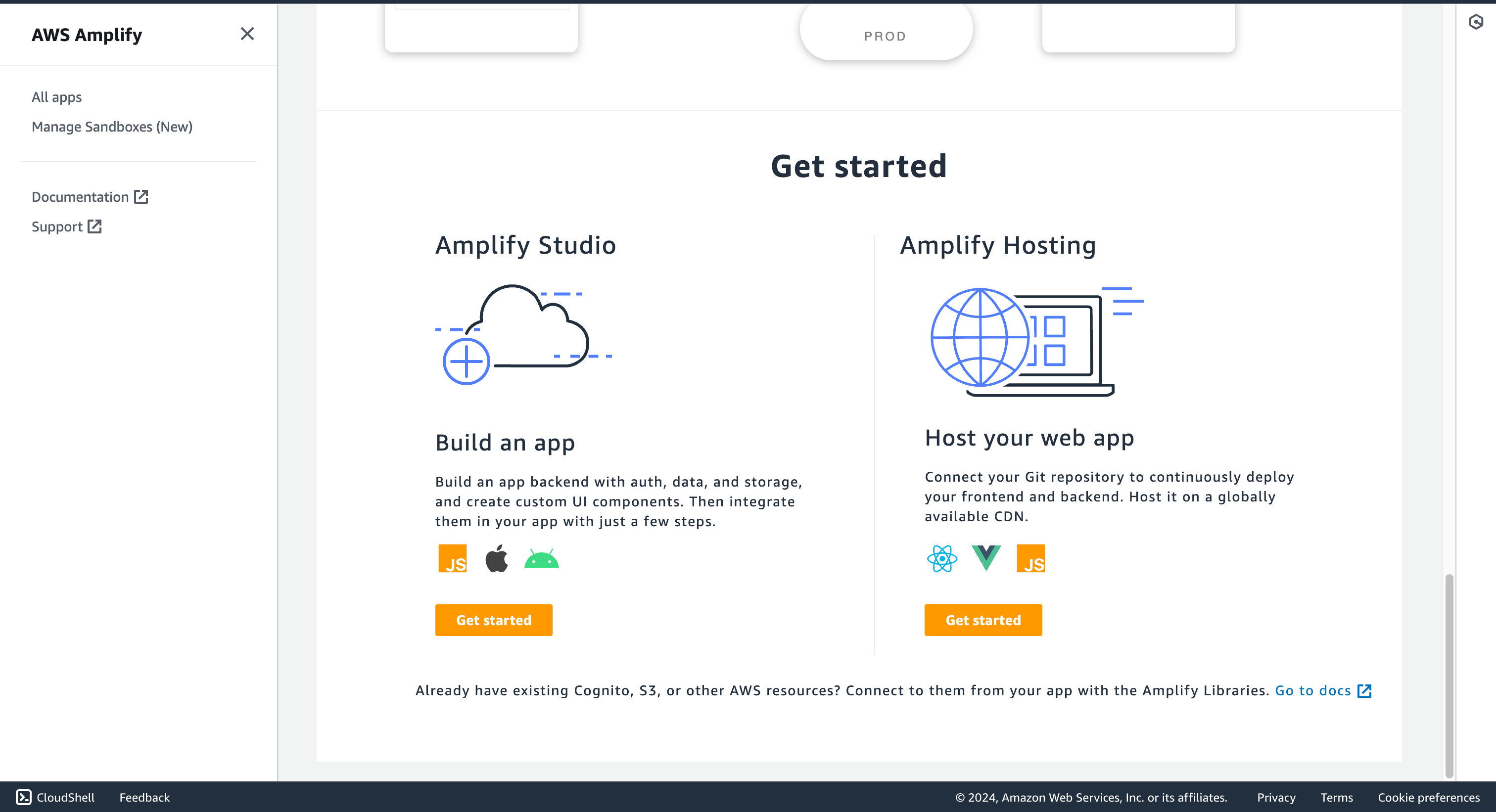
- Select GitHub as the source of your Git repository.
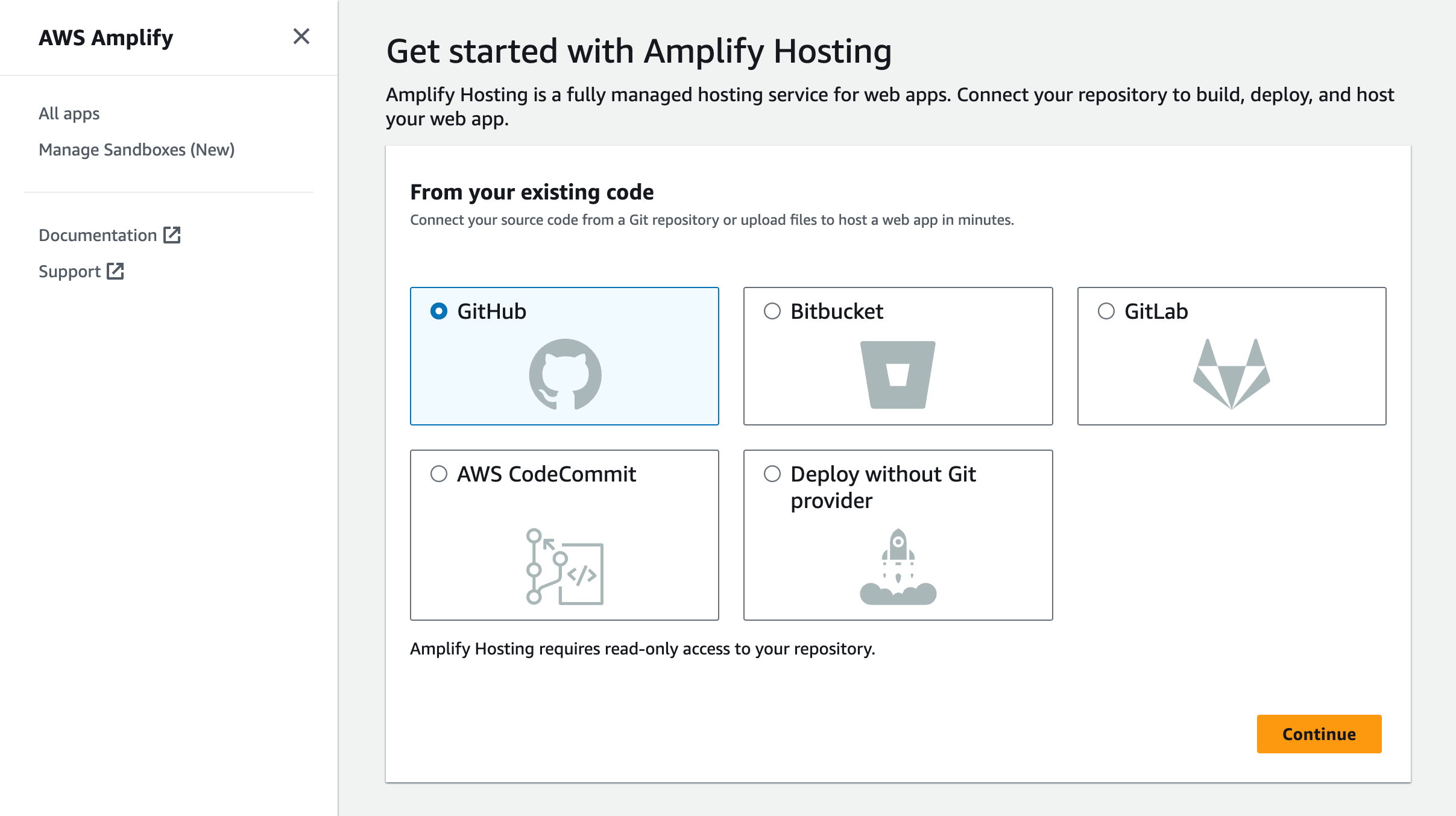
- Link the new project to the GitHub repository you just created.
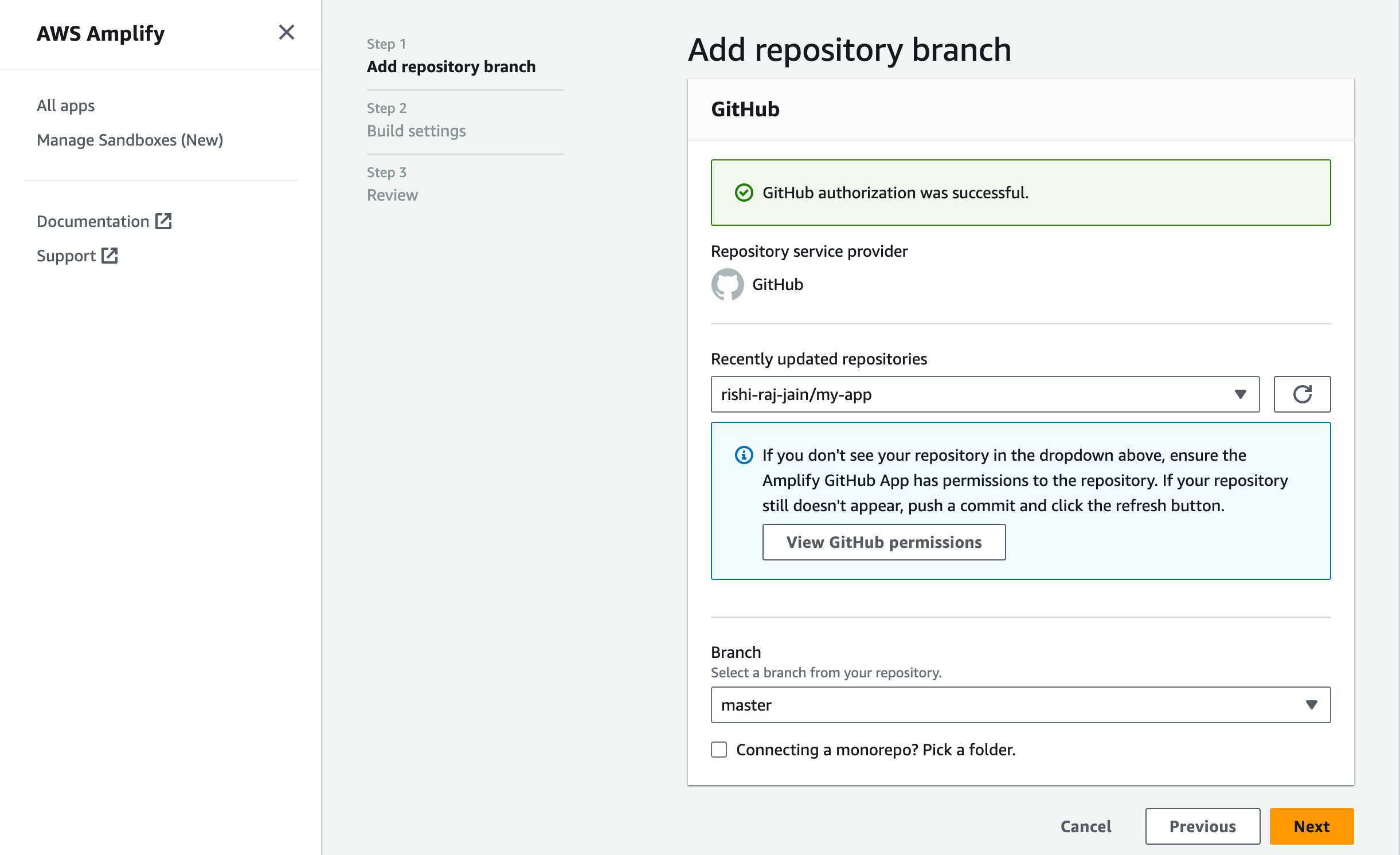
- Give a name to your project, and click on Advanced Settings.
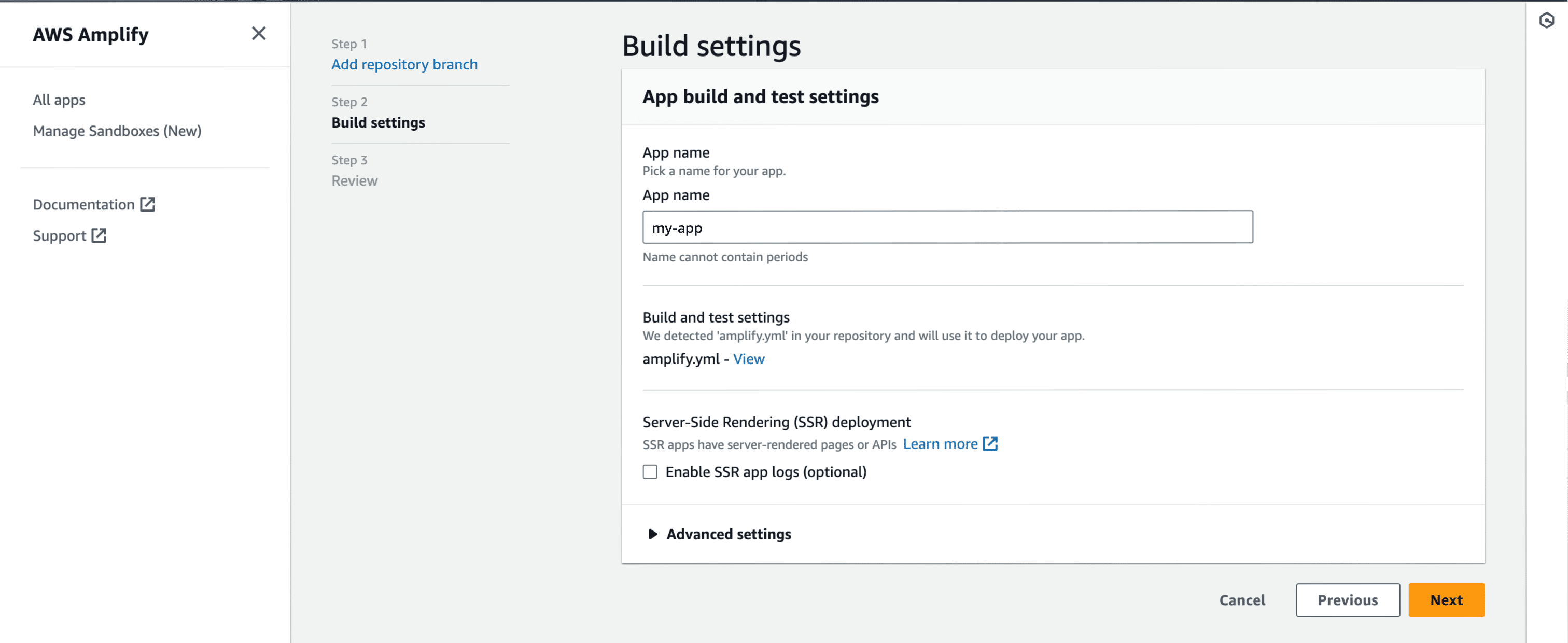
- In Advanced Settings, update the Environment Variables to match those in your local
.envfile, andPORTas 3000. Click Next to proceed.
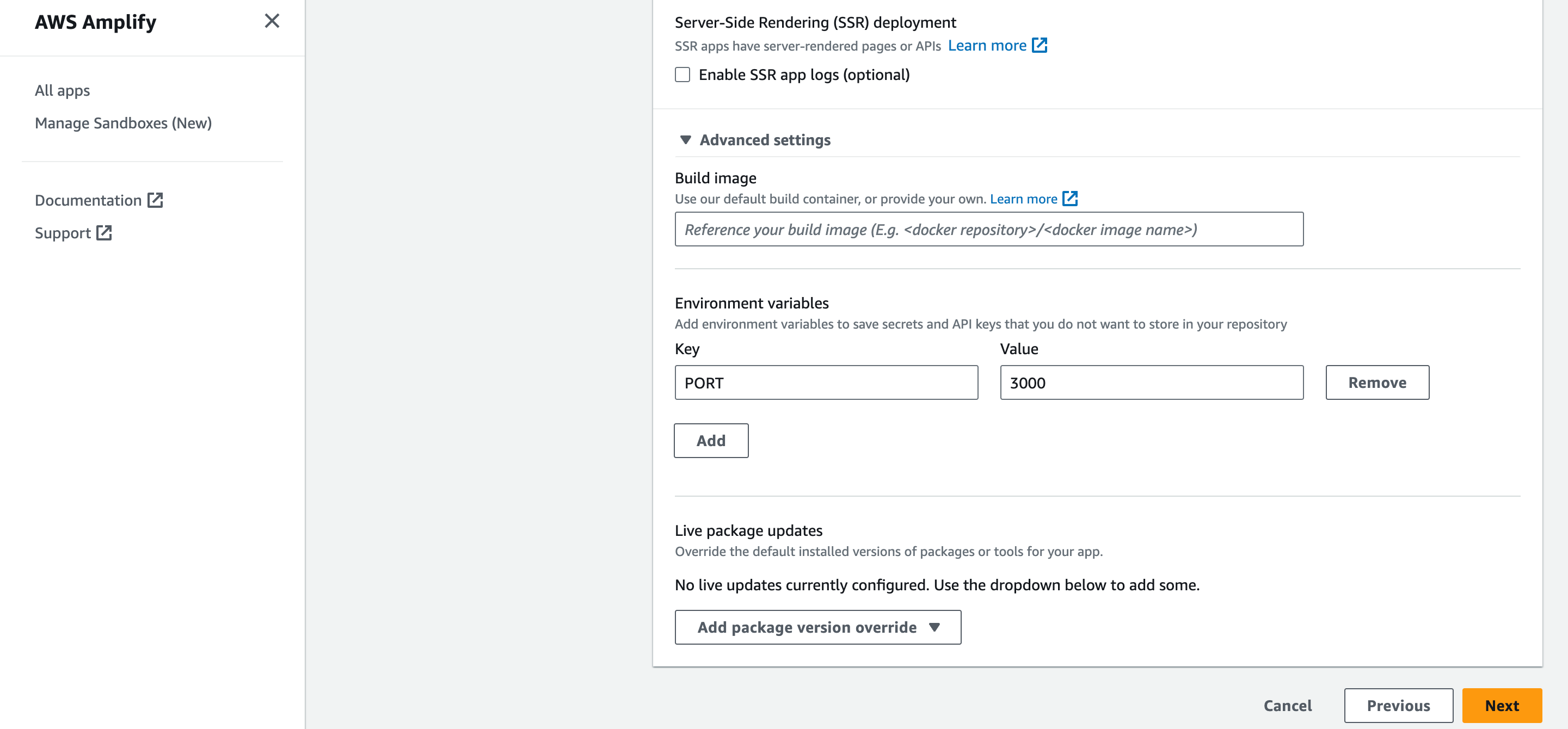
- Click Save and Deploy to deploy your website.
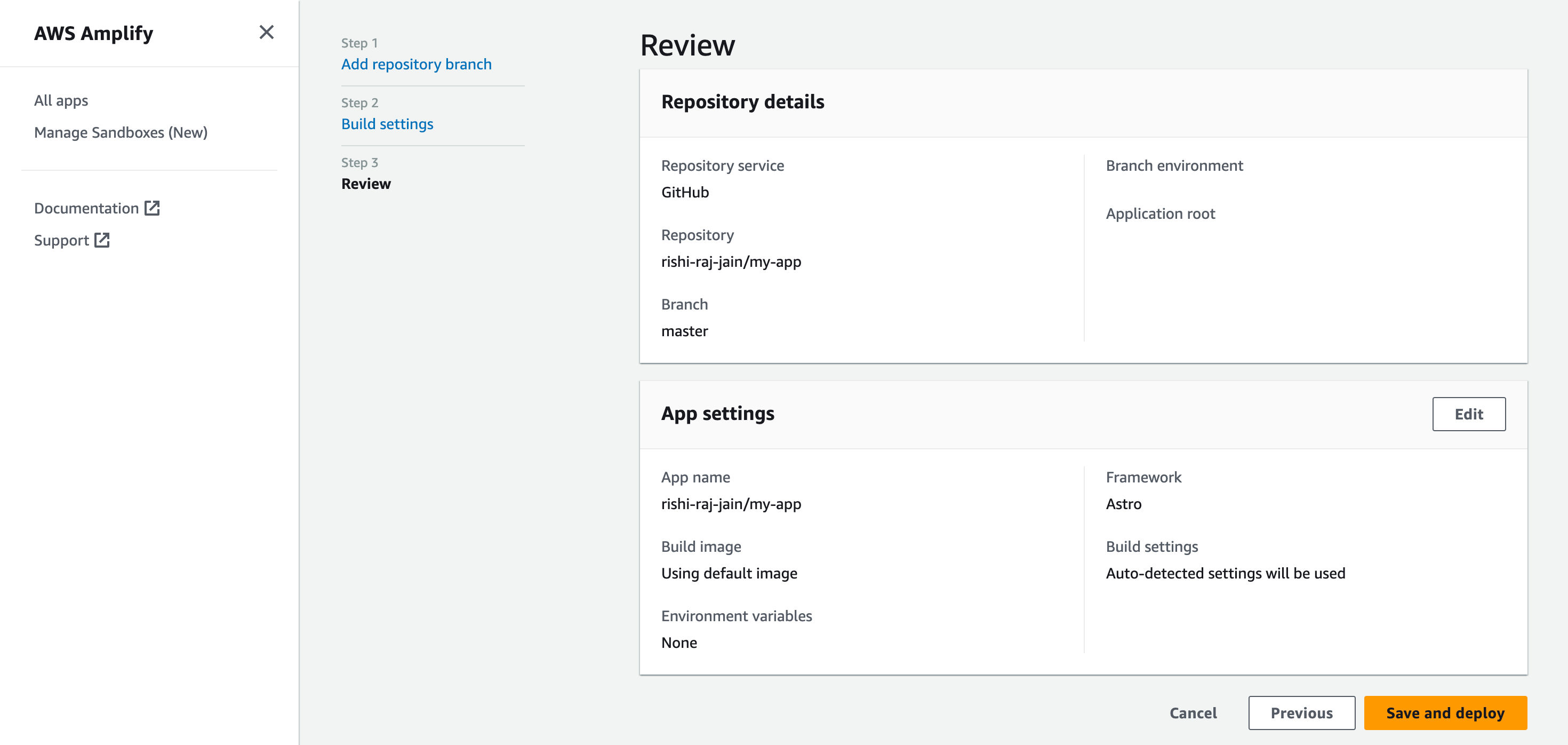
- Grab the deployment URL under the Domain title in the succesful build information.
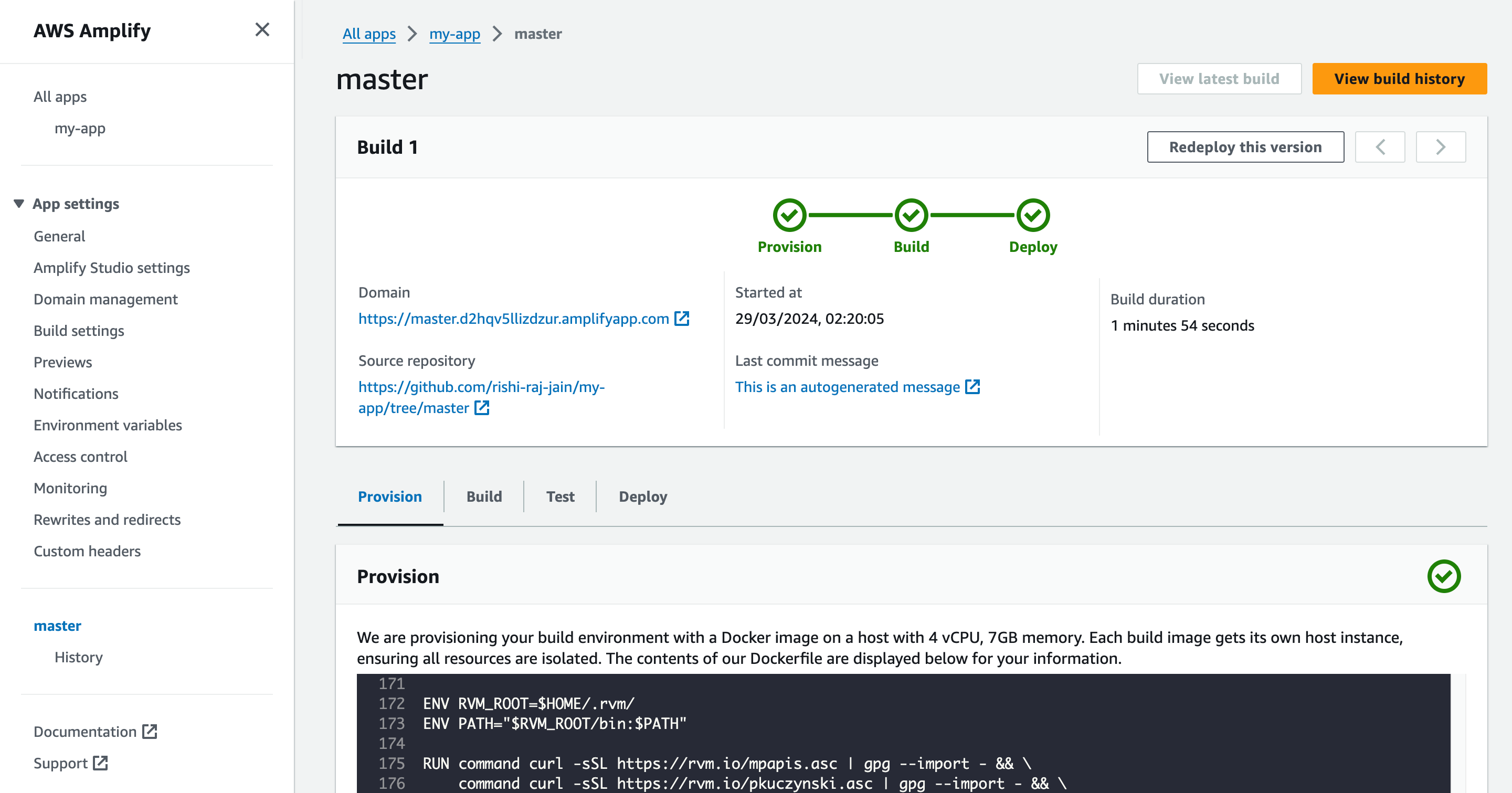
Conclusion
Yay! You’ve now an Astro project that automatically deploys to AWS Amplify upon Git push.
If you have any questions or comments, feel free to reach out to me on Twitter.


