
Rate limiting is essential for protecting your APIs and pages from abuse, brute force attacks, and excessive usage. Cloudflare Workers provides a built-in Rate Limiting binding that makes it easy to implement rate limiting at the edge.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to implement rate limiting in Astro using Cloudflare’s Rate Limiting API, both globally via middleware and at the endpoint level.
Prerequisites
- Node.js 20 or later
- A Cloudflare account
Create a new Astro application
Let’s get started by creating a new Astro project. Execute the following command:
npm create astro@latest my-ratelimit-astro-appWhen prompted, choose:
Use minimal (empty) templatewhen prompted on how to start the new project.Yeswhen prompted to install dependencies.Yeswhen prompted to initialize a git repository.
Once that’s done, move into the project directory:
cd my-ratelimit-astro-appnpm install wranglernpm run devThe app should be running on localhost:4321.
Integrate Cloudflare adapter in your Astro project
To deploy your Astro project to Cloudflare Workers and use Cloudflare KV, you need to install the Cloudflare adapter. Execute the command below:
npx astro add cloudflare --yesUpdate astro.config.mjs to have output as server:
import { defineConfig } from 'astro/config';import cloudflare from '@astrojs/cloudflare';
export default defineConfig({ output: 'server', adapter: cloudflare()});Configure the Rate Limiting binding
Add the rate limiting binding to your wrangler.jsonc:
{ // ... "ratelimits": [ { "namespace_id": "1001", "name": "MY_RATE_LIMITER", "simple": { "limit": 100, "period": 60 } } ]}This configuration:
- Creates a rate limiter named
MY_RATE_LIMITER - Allows 100 requests per 60 seconds per unique key
- Uses
namespace_idto isolate rate limit counters
Update your src/env.d.ts to add TypeScript definitions:
/// <reference types="astro/client" />
type RateLimiter = { limit: (options: { key: string }) => Promise<{ success: boolean }>}
type ENV = { MY_RATE_LIMITER: RateLimiter}
type Runtime = import('@astrojs/cloudflare').Runtime<ENV>
declare namespace App { interface Locals extends Runtime {}}Rate Limiting in Astro Middleware
To apply rate limiting globally (or to specific routes), create a middleware file at src/middleware.ts:
import { defineMiddleware } from 'astro:middleware'
// Routes to rate limitconst RATE_LIMITED_ROUTES = ['/']
export const onRequest = defineMiddleware(async (context, next) => { const { url, request, locals } = context const pathname = url.pathname
// Check if route should be rate limited const shouldRateLimit = RATE_LIMITED_ROUTES.some((route) => pathname === (route) )
if (!shouldRateLimit) { return next() }
// Skip if rate limiter is not available (local dev) const rateLimiter = locals.runtime?.env?.MY_RATE_LIMITER if (!rateLimiter) { console.log('[Rate Limit] Binding not available, skipping') return next() }
// Use client IP as the rate limit key const clientIP = request.headers.get('CF-Connecting-IP') || 'unknown'
try { const { success } = await rateLimiter.limit({ key: clientIP })
if (!success) { return new Response( JSON.stringify({ error: 'Too Many Requests', message: 'Rate limit exceeded. Please try again later.', }), { status: 429, headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Retry-After': '60', }, } ) } } catch (error) { console.error('[Rate Limit] Error:', error) // On error, allow the request (fail open) }
return next()})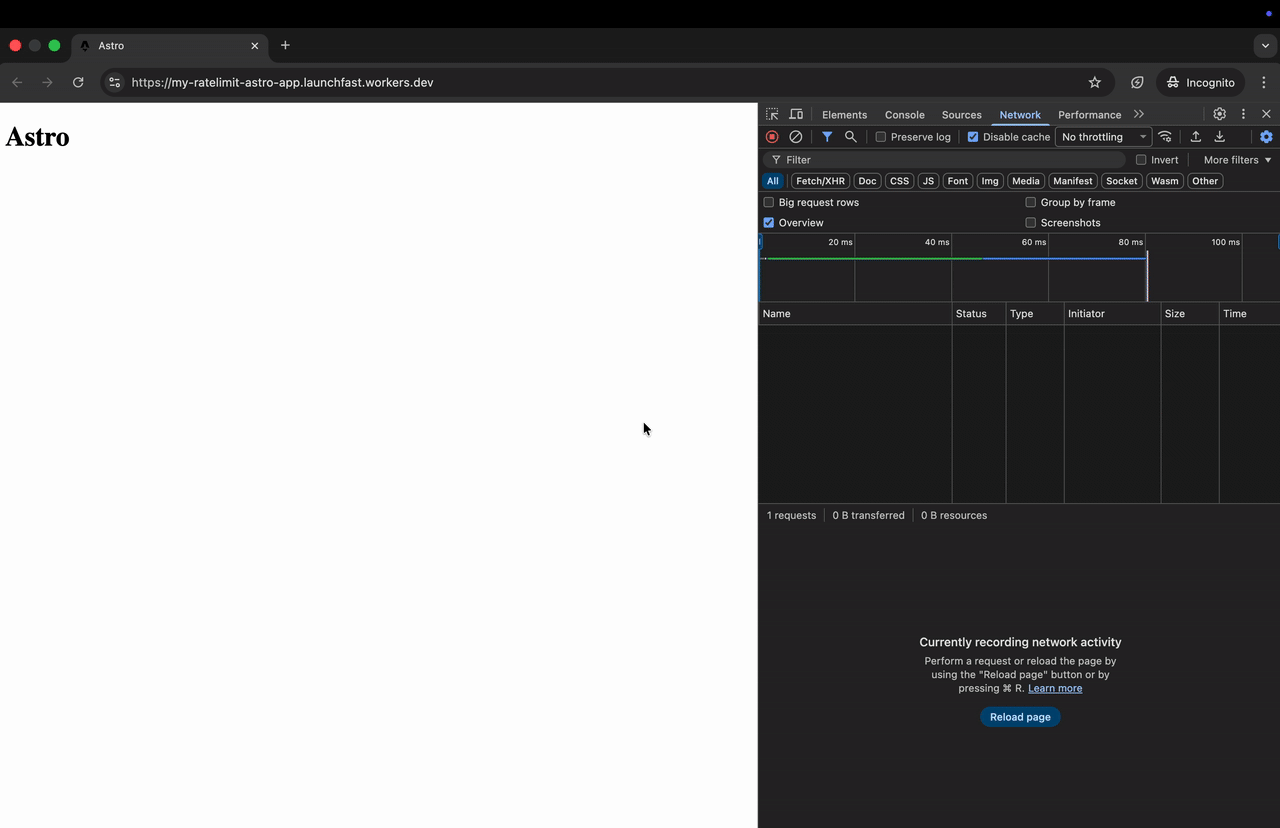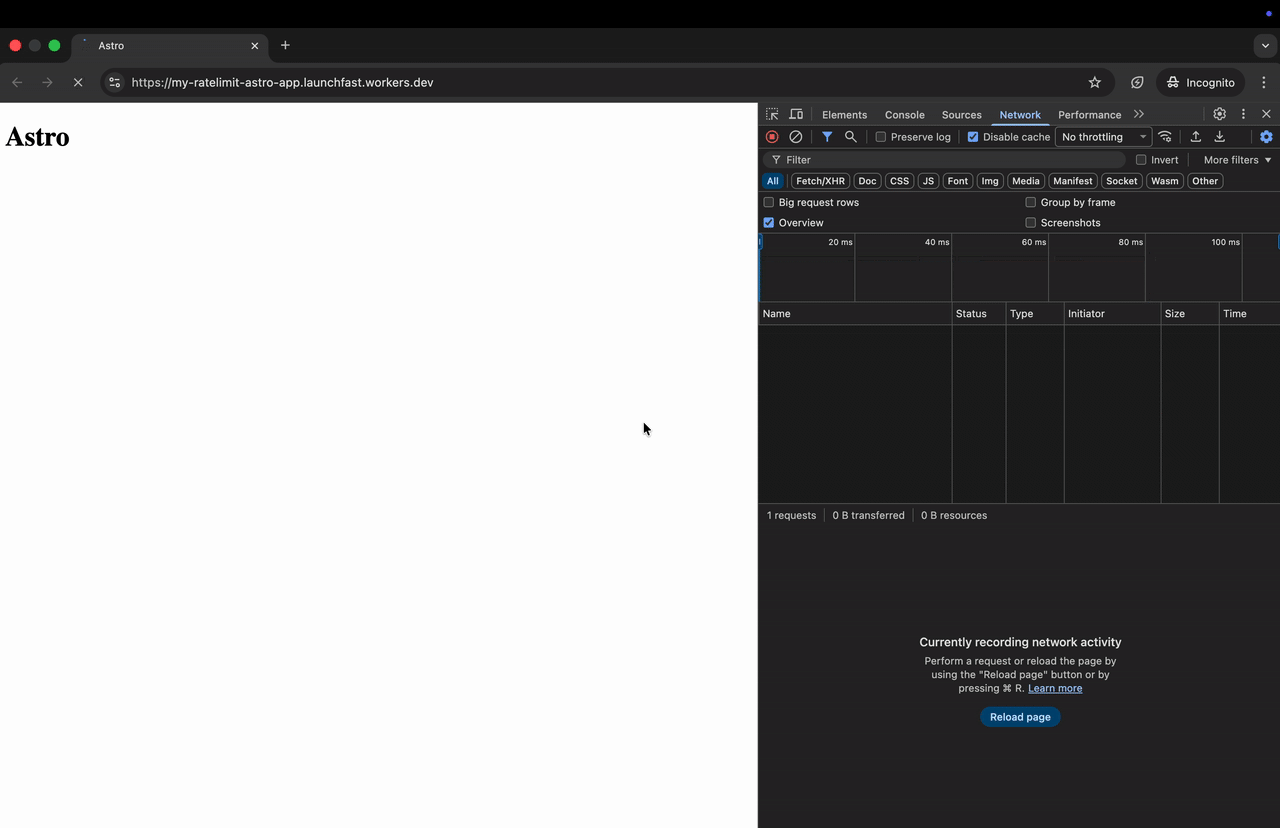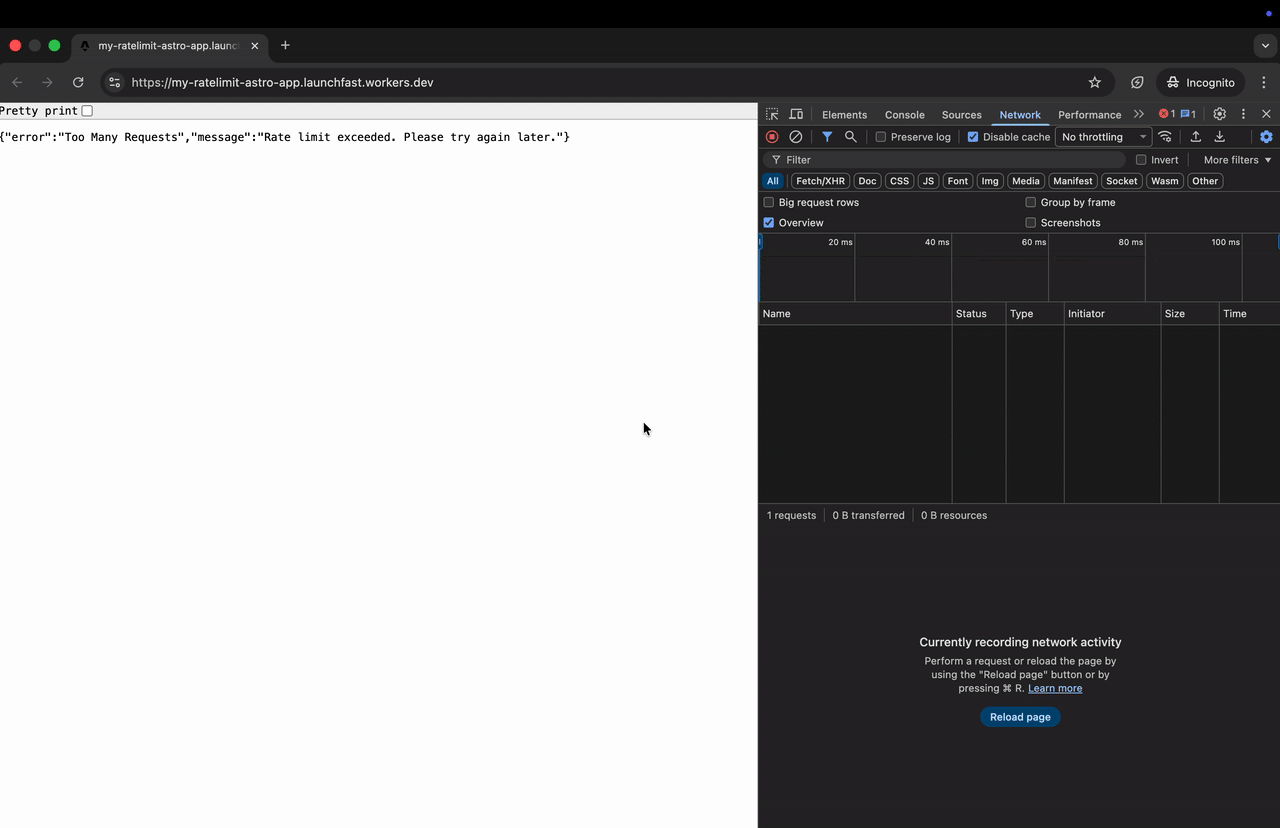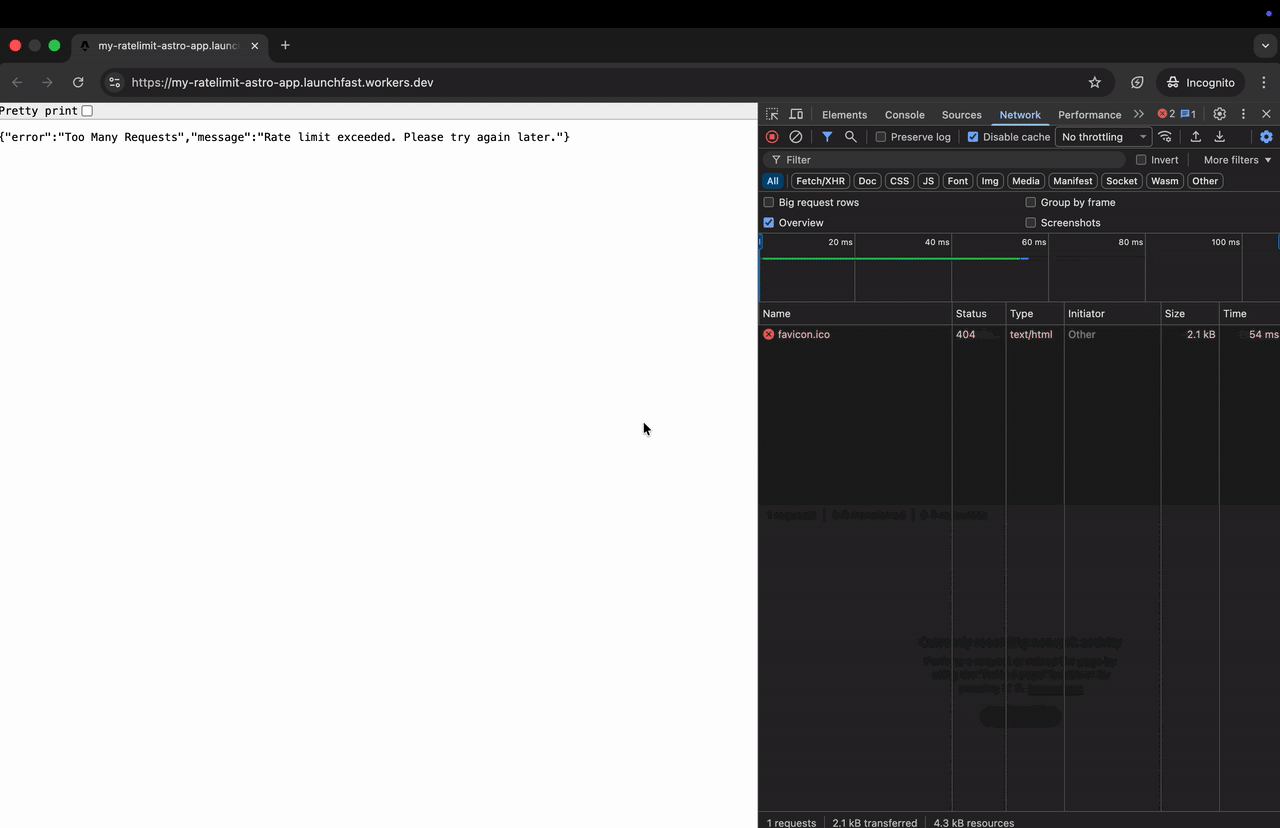
This middleware:
- Checks if the current route should be rate limited
- Uses the client’s IP address as the rate limit key
- Returns a
429 Too Many Requestsresponse when the limit is exceeded
Rate Limiting in an API Endpoint
For more granular control, apply rate limiting directly in your API endpoints. Create src/pages/api/data.ts:
import type { APIContext } from 'astro'
export async function GET({ request, locals }: APIContext) { const rateLimiter = locals.runtime?.env?.MY_RATE_LIMITER
if (rateLimiter) { const clientIP = request.headers.get('CF-Connecting-IP') || 'unknown'
const { success } = await rateLimiter.limit({ key: clientIP })
if (!success) { return new Response( JSON.stringify({ error: 'Rate limit exceeded' }), { status: 429, headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }, } ) } }
// Your endpoint logic here return new Response( JSON.stringify({ message: 'Success', data: { timestamp: Date.now() } }), { status: 200, headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }, } )}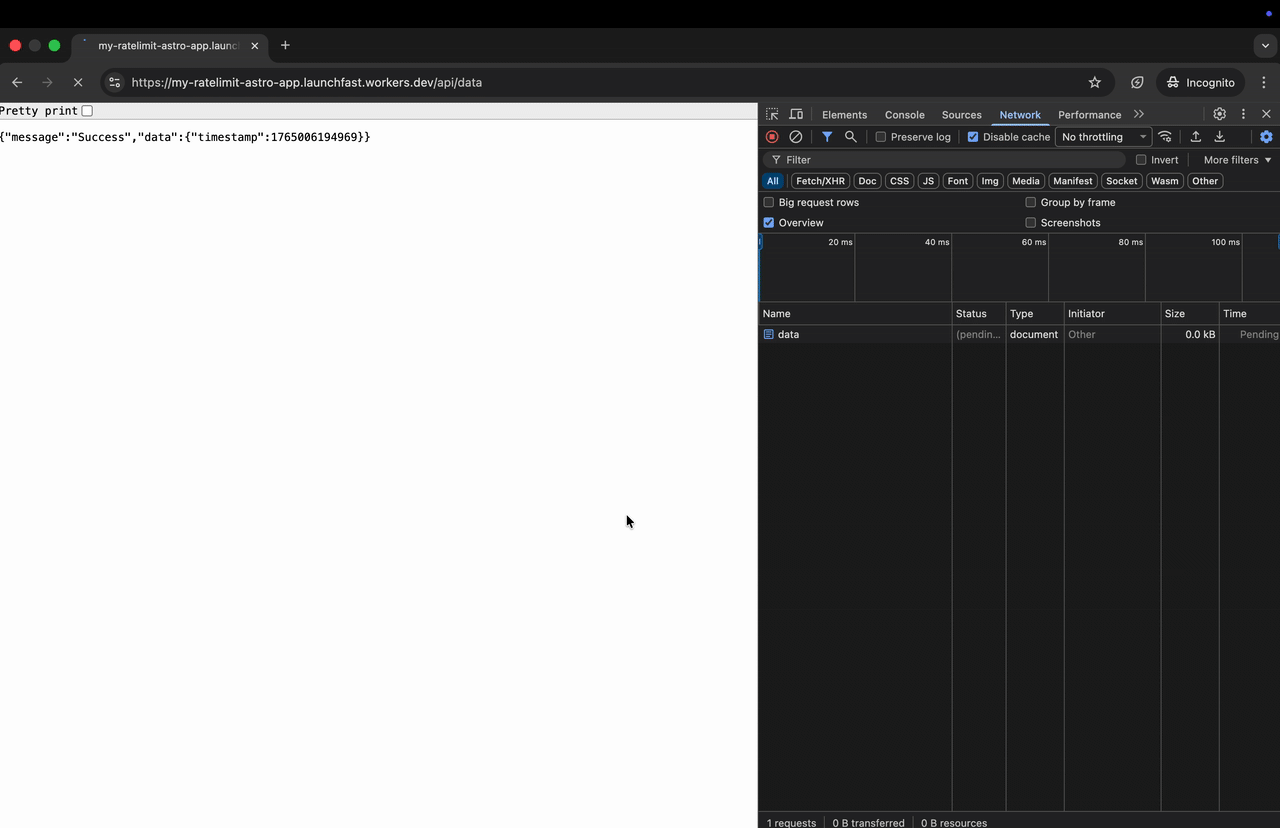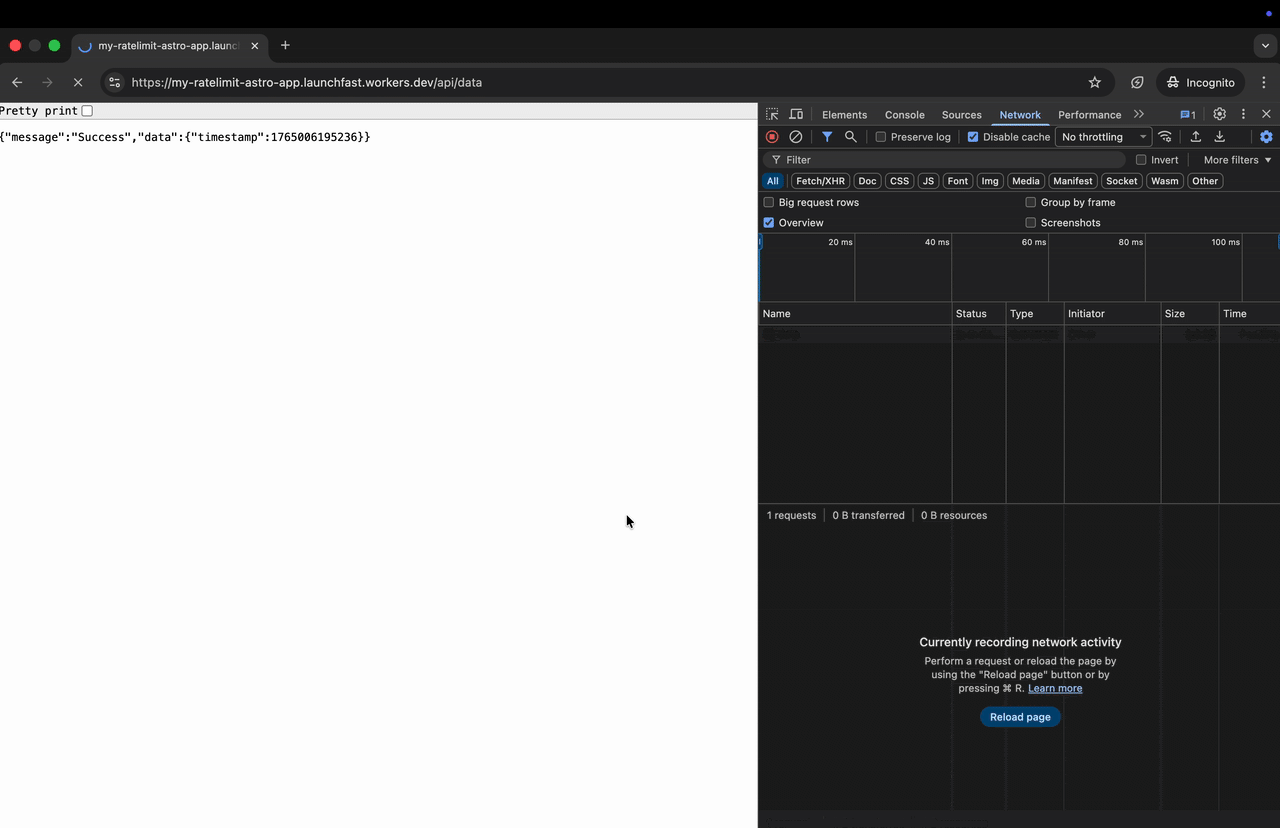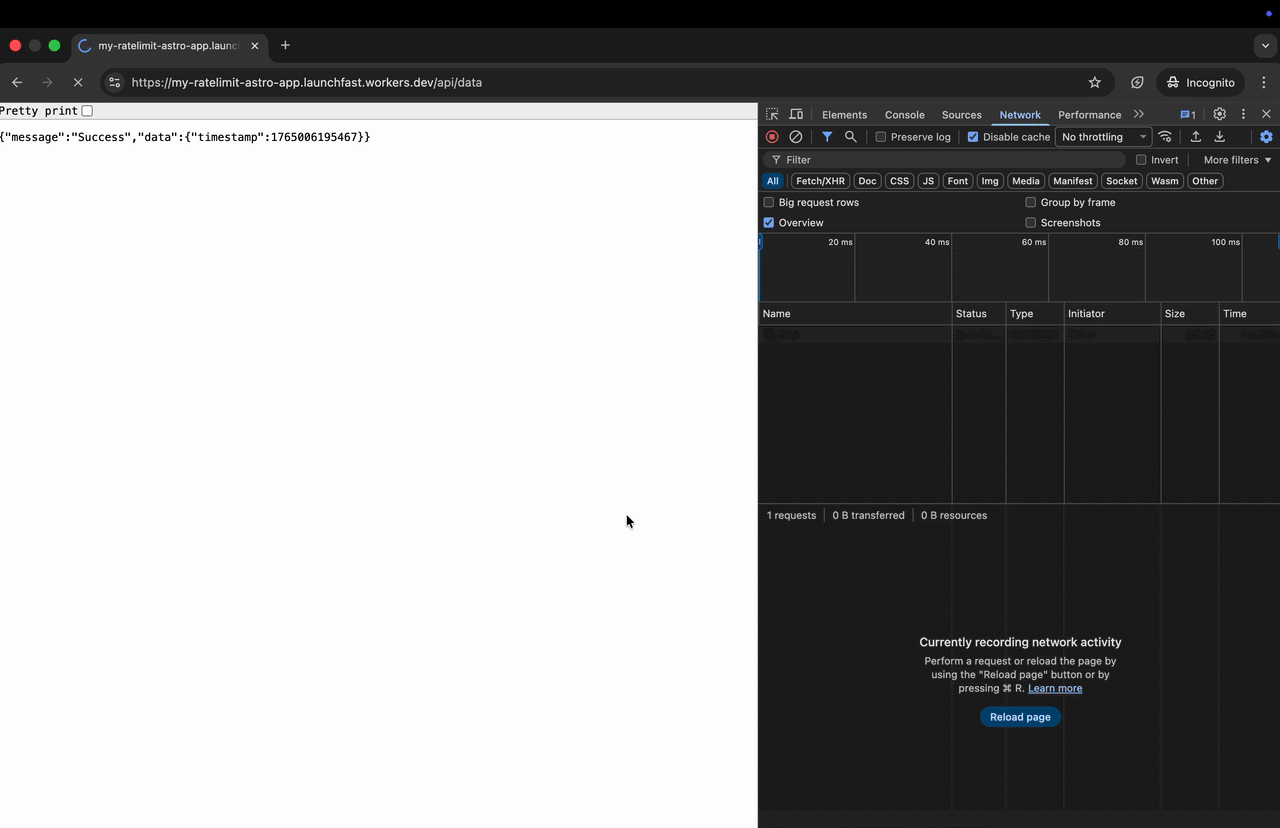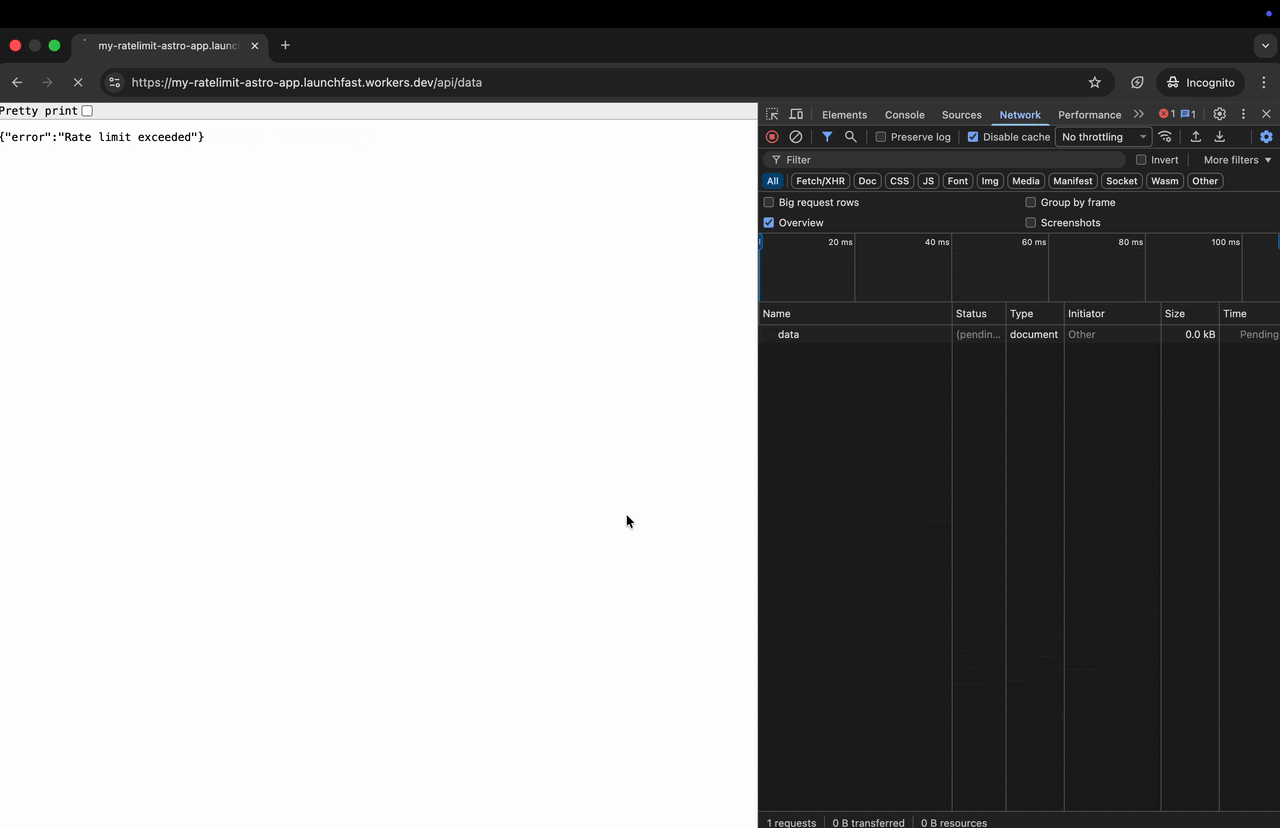
This endpoint:
- Uses the client’s IP address as the rate limit key
- Returns a
429 Rate Limit Exceededresponse when the limit is exceeded
Custom Rate Limit Keys
You can use different keys for different rate limiting strategies:
// Rate limit by user ID (for authenticated routes)const userId = locals.user?.idconst { success } = await rateLimiter.limit({ key: `user:${userId}` })
// Rate limit by IP + endpoint combinationconst key = `${clientIP}:${url.pathname}`const { success } = await rateLimiter.limit({ key })
// Rate limit by API keyconst apiKey = request.headers.get('X-API-Key') || 'anonymous'const { success } = await rateLimiter.limit({ key: `api:${apiKey}` })Deploy to Cloudflare Workers
Deploy your rate-limiting enabled Astro application to production:
# Build the projectnpm run build
# Deploy to Cloudflare Workersnpx wrangler deployConclusion
By implementing rate limiting with Cloudflare Workers in your Astro app, you effectively block abusive requests - such as brute force attacks, API overuse, and DDoS attempts at the edge. This improves both your application’s security and performance by stopping threats before they hit your application logic.


